Last Updated on April 15, 2024
As you probably know, the majority of SEO campaigns tend to revolve around the Google algorithm. While most search engines follow in Google’s footsteps algorithm and update-wise, Baidu however, does not. With 80% of searches made in China being through Baidu, it’s not only a force to be reckoned with, ignoring it as a major player would be a huge mistake. If you’ve been tasked with optimizing for Baidu, listen up; the search engine shares a lot of similarities to Google, but comes with some noteworthy differences as well. Here\’s our guide to Baidu SEO and how to get ahead of the competition!
1.Registering For An ICP Record
The first step you’ll need to take if you’re operating a website in China is to register for an ICP record. An ICP record (internet content provider) is essentially a state-issued registration number which allows you to legally host your site on a Chinese server. ICP numbers are only granted to locally-owned companies, so if you’re a foreign-owned company you’ll have to look into renting an ICP from a local provider.
Every website hosted within a mainland Chinese server is legally obligated to apply for and receive one of these numbers before the site is pushed live. There’s really no way of getting around this law, especially since it’s enforced at the hosting level. You can usually find ICP numbers displayed next to a small icon in the footer of websites.

For example, here’s a screenshot of the ICP number on SkateHere.com (the first skateboarding website in China).

Here’s the ICP number for the popular video sharing site, Youku.

And the ICP number in the footer of the classifieds site, 58.com
There are two types of ICP records, commercial and individual. For a commercial record, you\’re required to obtain a Chinese business registration before applying. If you’re looking to get an individual ICP record, you must be willing to provide an address and phone number in China. While having an ICP record isn’t a requirement for your site to be accessed within China, it’s certainly something that Baidu takes into account and favors for when it comes to ranking site\’s within the SERPS. Having a locally hosted website will also grant you a faster website, which Baidu looks upon quite favorably over the slower, foreign-hosted sites.
2.Registering Your Domain & URL Best Practices
Another big consideration for increasing the likelihood of high rankings is your domain and the domain suffix. Both Baidu and Chinese internet users prefer to see locally-hosted domains with .cn/.com.cn extensions. If hosting in mainland China isn’t an option, it’s highly recommended to at least register a domain with the .cn/.com.cn suffix.
Baidu, just like Google and human web users, prefers readable urls as opposed to a mumble jumble of numbers and letters. So, having a semantic URL is of the essence if you want to rake in those ranking points.
Example:
Semantic URL:
Non-Semantic:
3.Mobile Optimization
If you haven’t heard, worldwide mobile & tablet usage has finally eclipsed desktop use and shows no signs of slowing down. We’ve been talking about it for years and now it\’s happened, so having a mobile-friendly site is a must these days.
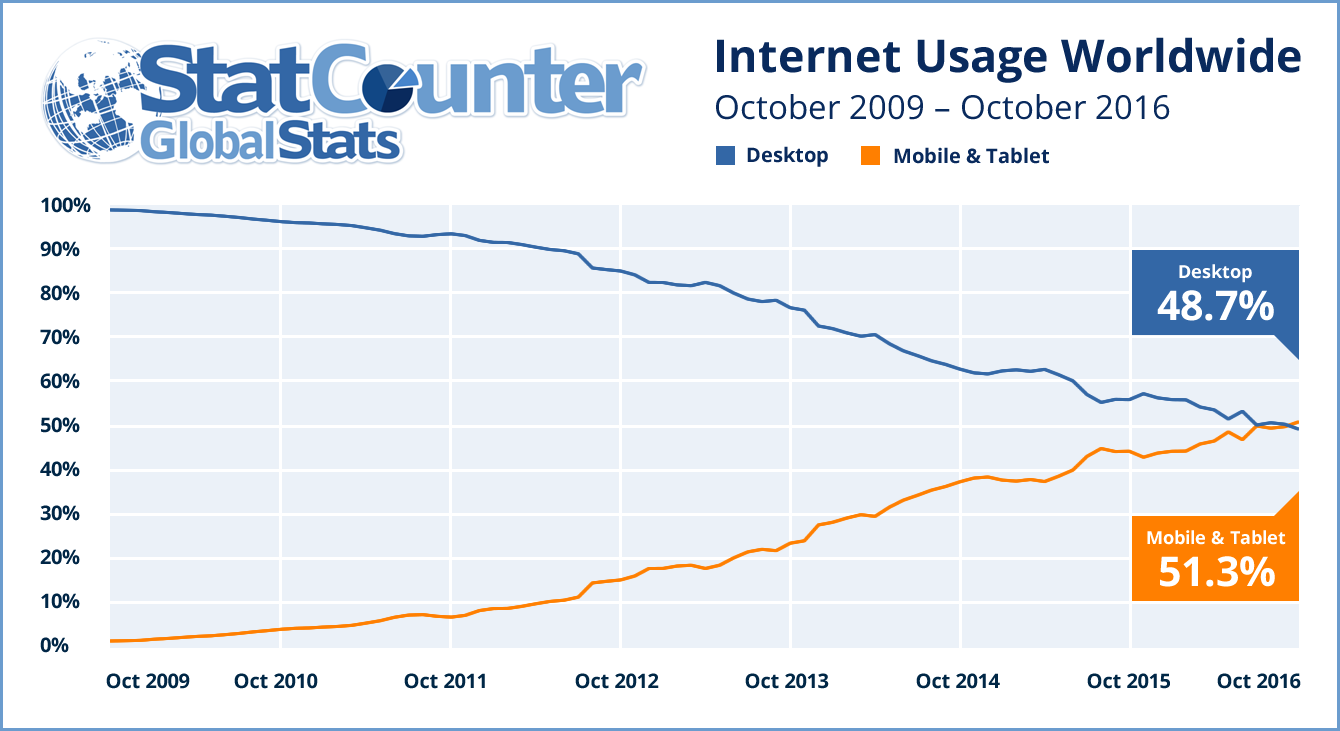
If you’ve ever been to China, you’ve surely noticed that nearly everyone around you has a smartphone, commanding most of their attention at any given time. Baidu knows this. A mobile-friendly site is so important to them, so much that if your site isn’t properly optimized, Baidu will optimize it for you. While you might be quick to thank them and write off doing your own mobile optimization, I strongly encourage you to not cut corners here. If you do, Baidu will decide what is shown on your site’s mobile version and how it reacts.
4.Keywords & Content
Similar to Google, Baidu also takes into account keywords for when it ranks a page. The biggest difference here is keywords and the keyword tools you’d use for Google are not the same for Baidu. Google’s keyword tool and the keywords it provides won’t directly translate to Chinese correctly. If your aim is to have a multilingual website, it’s best to work with a human translator with native-level Mandarin.
With that said, sites written in simplified Chinese tend to work best. All copy should be written in simplified Chinese, including the metadata and title tags. You should try to avoid using Roman characters, except for within the URL. The slug should be written out in Pinyin (the way Chinese words would be written using Roman characters).
Just like Google, Baidu takes into account many of the same standards for assessing content and copy. You must avoid duplicate content like the plague; ensure that each page has at least 300 words of quality, useful copy; and be sure to write for the user first…don’t worry about keyword density or overthink things too much.
Additionally, make sure to keep your site’s copy fresh and consistently updated. Not only does this mean maintaining a regular blog, but also making sure to revisit all pages on your site and add to or revamp them as needed.
Another thing to consider content-wise is the large and growing list of blacklisted words. Censorship is heavy in China, so any page that has blacklisted words on it will be de-indexed by Baidu (if not your whole site). You can do a quick search online for a complete list of blacklisted words (hint: Wikipedia) to keep handy while writing content. It’s also a good idea to proactively monitor your site’s comments section (if applicable) and immediately remove any sensitive comments or those containing blacklisted words or phrases.
5.Meta Data, Descriptions & Titles
Meta titles and descriptions should be filled out and unique for each page on your site. One big difference worth noting though is that while other search engines no longer consider meta keywords, Baidu does. So make sure to do your keyword research and fill out those meta keywords for each page on your site!
6.Technical SEO
1)Inbound Links
Let’s start off here with one of the biggest differences between the Google and Baidu algorithms. We know acquiring paid links or participating in link schemes of any kind is a big “no-no” in the Google world, however things are quite the opposite for Baidu. While they’ve been taking strides to improve in this area for some time, Baidu is still rather far behind when it comes to evaluating inbound links. Historically they’ve been known to favor quantity over quality, which is why many folks looking for quick gains participate in link building schemes. We expect this area to be cleaned up, so it’s advisable to avoid the temptation of purchasing links.
2)Site Structure & Internal Linking
Baidu’s spiders and crawling power isn’t as refined as Google, so having pages easily accessible with the fewest possible clicks will likely yield a better crawl. Layout your site with a simple, flat structure make sure you link to relevant pages when possible. Anchor text is also highly important here, so having relevant anchor text on both your internal and external links is seen very favorably in the eyes of Baidu.
3)External Links
Regardless if you’re optimizing for Baidu or Google, linking to other high-quality sites is seen as best practice. However, Baidu prefers to see links pointing to other Chinese sites whereas Google doesn’t appear to have country restrictions when it comes to external links. While Baidu will take links to trusted foreign sites into consideration, they certainly give preference to trustworthy China-hosted sites.
4)Image ALT Attribute
The only way Baidu can rank images is based on their individual ALT attribute, so having an ALT attribute written in Chinese is crucial.
5.Some Parting Words
So as you can see, getting ready for launching a Baidu SEO campaign can be a bit different than your average Google-targeted plan. One of the biggest reasons companies invest in Baidu is that the search engine has a complete understanding of the Chinese market, as well as their consumers and their unique searching habits. Hopefully, the points we’ve discussed today will help you get started on your journey to SEO success on Baidu. Keep in mind, these are just starting points and not the be-all, end-all for a successful Baidu campaign.

